az-900-notes
2. Describe Core Azure Services (30-35%)
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/learn/modules/define-core-azure-services-products/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/guide/technology-choices/compute-decision-tree
2.1. Describe the core Azure architectural components
2.1.A. describe Regions
A region is a set of datacenters deployed within a latency-defined perimeter and connected through a dedicated regional low-latency network.
- Regions provide customers the flexibility and scale needed to bring applications closer to their users.
- Regions preserve data residency and offer comprehensive compliance and resiliency options for customers.
A geography is a discrete market, typically containing two or more regions, that preserves data residency and compliance boundaries.
Special Azure regions
- US DoD Central, US Gov Virginia, US Gov Iowa and more
- China East, China North and more: unique partnership between Microsoft and 21Vianet
Region Pairs
- Each Azure region is paired with another region within the same geography (such as US, Europe, or Asia) at least 300 miles away, which together make a region pair.
- Physical isolation. When possible, Azure prefers at least 300 miles of separation between datacenters in a regional pair, although this isn’t practical or possible in all geographies.
- Platform-provided replication. Some services such as Geo-Redundant Storage provide automatic replication to the paired region.
- Region recovery order. In the event of a broad outage, recovery of one region is prioritized out of every pair. Applications that are deployed across paired regions are guaranteed to have one of the regions recovered with priority.
- Sequential updates. Planned Azure system updates are rolled out to paired regions sequentially (not at the same time) to minimize downtime, the effect of bugs, and logical failures in the rare event of a bad update.
- Data continues to reside within the same geography as its pair (except for Brazil South) for tax and law enforcement jurisdiction purposes.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/discuss-core-azure-architectural-components/3-explore-region-pairs
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/best-practices-availability-paired-regions#what-are-paired-regions?azure-portal=true
2.1.B. describe Availability Zones
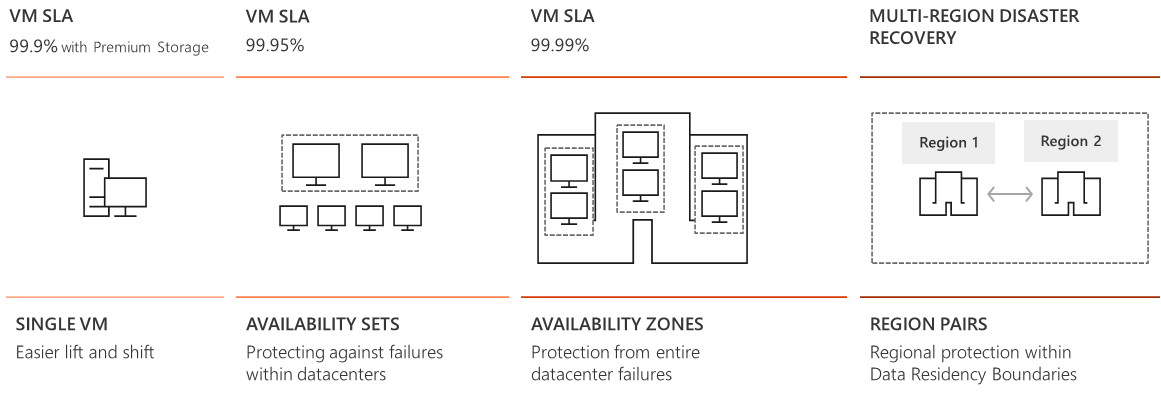
Availability Zones are physically separate locations within an Azure region.
Each Availability Zone is made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking.
Availability Zone features
- Each availability zone is an isolation boundary containing one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking.
- If one availability zone goes down, the other continues working.
- The availability zones are typically connected to each other through very fast, private fiber-optic networks.
- Availability zones allow customers to run mission-critical applications with high availability and low-latency replication.
- Availability zones are offered as a service within Azure, and to ensure resiliency, there’s a minimum of three separate zones in all enabled regions.
Availability Zones are primarily for VMs, managed disks, load balancers, and SQL databases. Azure services that support Availability Zones fall into two categories:
- Zonal services – you pin the resource to a specific zone (for example, virtual machines, managed disks, IP addresses)
- Zone-redundant services – platform replicates automatically across zones (for example, zone-redundant storage, SQL Database).
Availability sets are a way for you to ensure your application remains online if a high-impact maintenance event is required, or if a hardware failure occurs.
- Availability sets are made up of Update domains (UD) and Fault domains (FD).
- Update domains. When a maintenance event occurs (such as a performance update or critical security patch applied to the host), the update is sequenced through update domains. Update domains are a logical section of the datacenter, and they are implemented with software and logic.
- Fault domains. Fault domains provide for the physical separation of your workload across different hardware in the datacenter. This includes power, cooling, and network hardware that supports the physical servers located in server racks. In the event the hardware that supports a server rack becomes unavailable, only that rack of servers would be affected by the outage.
2.1.C. describe Resource Groups
- A resource group is a unit of management for your resources in Azure.
- A container that allows you to aggregate and manage all the resources required for your application in a single manageable unit.
- All resources must be in a resource group and a resource can only be a member of a single resource group.
- Many resources can be moved between resource groups with some services having specific limitations or requirements to move.
- Resource groups can’t be nested.
- Allows you to manage the application collectively over its lifecycle.
Manage and apply the following resources at resource group level:
- Metering and billing
- Policies
- Monitoring and alerts
- Quotas
- Access control
2.1.D. describe Azure Resource Manager
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/discuss-core-azure-architectural-components/9-explore-azure-resource-manager
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-resource-manager/management/overview
- Azure Resource Manager is a management layer in which resource groups and all the resources within it are created, configured, managed, and deleted.
- It provides a consistent management layer which allows you automate the deployment and configuration of resources using different automation and scripting tools, such as Microsoft Azure PowerShell, Azure Command-Line Interface (Azure CLI), Azure portal, REST API, and client SDKs.
With Azure Resource Manager, you can:
- Deploy Application resources. Update, manage, and delete all the resources for your solution in a single, coordinated operation.
- Organize resources. Manage your infrastructure through declarative templates rather than scripts. You can view which resources are linked by a dependency, and you can apply tags to resources to categorize them for management tasks, such as billing.
- Control access and resources. You can control who in your organization can perform actions on the resources. You manage permissions by defining roles, adding users or groups to the roles, and applying policies at resource group level. Examples of elements you may wish to control are: enforcing naming convention on resources, limiting which types and instances of resources can be deployed, or limiting which regions can host a type of resource.
The benefits of using Resource Manager
- Manage your infrastructure through declarative templates rather than scripts.
- Deploy, manage, and monitor all the resources for your solution as a group, rather than handling these resources individually.
- Redeploy your solution throughout the development lifecycle and have confidence your resources are deployed in a consistent state.
- Define the dependencies between resources so they’re deployed in the correct order.
- Apply access control to all services because Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is natively integrated into the management platform.
- Apply tags to resources to logically organize all the resources in your subscription.
- Clarify your organization’s billing by viewing costs for a group of resources sharing the same tag.
Resource Manager template - A JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) file that defines one or more resources to deploy to a resource group, subscription, management group, or tenant. The template can be used to deploy the resources consistently and repeatedly. See Template deployment overview.
2.1.E. describe the benefits and usage of core Azure architectural components
2.2. Describe some of the core products available in Azure
2.2.A. describe products available for Compute such as Virtual Machines, Virtual Machine Scale Sets, App Services, Azure Container Instances (ACI) and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Azure Compute Services
Azure virtual machines
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/
- Create and use virtual machines in the cloud.
- Similar to EC2 Instances (AWS)
- VM Pricing options:
- Pay as you go: Pay for compute capacity by the second, with no long-term commitment or upfront payments.
- Reserved VM instances: advanced purchase of VM for 1 or 3 years; up to 72% price savings.
- Spot pricing: Purcahse unused compute capacity, up to 90% price savings.
Virtual machine scale sets
- Azure compute resource that you can use to deploy and manage a set of identical VMs
- Docs: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machine-scale-sets/
- Similar to Auto Scaling (in AWS)
- Key benefits:
- Easy to create and manage multiple VMs.
Easy to maintain a consistent configuration across your environment; all VM instances are created from the same base OS image and configuration; support for Azure Load Balancer (layer 4 traffic) and Azure Application Gateway (layer 7 traffic load balancer). - Provides high availability and application resiliency
- Allows your application to automatically scale as resource demand changes
- Works at large-scale.
Scale sets support up to 1,000 VM instances. If you create and upload your own custom VM images, the limit is 600 VM instances.
- Easy to create and manage multiple VMs.
Differences between virtual machines and scale sets
| Scenario | Manual group of VMs | Virtual machine scale set |
|---|---|---|
| Add additional VM instances | Manual process to create, configure, and ensure compliance | Automatically create from central configuration |
| Traffic balancing and distribution | Manual process to create and configure Azure load balancer or Application Gateway | Can automatically create and integrate with Azure load balancer or Application Gateway |
| High availability and redundancy | Manually create Availability Set or distribute and track VMs across Availability Zones | Automatic distribution of VM instances across Availability Zones or Availability Sets |
| Scaling of VMs | Manual monitoring and Azure Automation | Autoscale based on host metrics, in-guest metrics, Application Insights, or schedule |
App services: quickly build, deploy, and scale enterprise-grade web, mobile, and API apps running on any platform.
- Similar to Elastic Beanstalk and LightSail (in AWS)
- Docs: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/app-service/
- Azure App Service is an HTTP-based service for hosting web applications, REST APIs, and mobile back ends.
- A fully managed platform for building, deploying and scaling your web apps.
- Host common app service styles, including: web apps; api apps; webjobs; mobile apps;
Key features of Azure App Service
- Multiple languages and frameworks. App Service has first-class support for ASP.NET, ASP.NET Core, Java, Ruby, Node.js, PHP, or Python. You can also run PowerShell and other scripts or executables as background services.
- DevOps optimization. Set up continuous integration and deployment with Azure DevOps, GitHub, BitBucket, Docker Hub, or Azure Container Registry. Promote updates through test and staging environments. Manage your apps in App Service by using Azure PowerShell or the cross-platform command-line interface (CLI).
- Global scale with high availability. Scale up or out manually or automatically. Host your apps anywhere in Microsoft’s global datacenter infrastructure, and the App Service SLA promises high availability.
- Connections to SaaS platforms and on-premises data. Choose from more than 50 connectors for enterprise systems (such as SAP), SaaS services (such as Salesforce), and internet services (such as Facebook). Access on-premises data using Hybrid Connections and Azure Virtual Networks.
- Security and compliance. App Service is ISO, SOC, and PCI compliant. Authenticate users with Azure Active Directory or with social login (Google, Facebook, Twitter, and Microsoft). Create IP address restrictions and manage service identities.
- Application templates. Choose from an extensive list of application templates in the Azure Marketplace, such as WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
- Visual Studio integration. Dedicated tools in Visual Studio streamline the work of creating, deploying, and debugging.
- API and mobile features. App Service provides turn-key CORS support for RESTful API scenarios, and simplifies mobile app scenarios by enabling authentication, offline data sync, push notifications, and more.
- Serverless code. Run a code snippet or script on-demand without having to explicitly provision or manage infrastructure, and pay only for the compute time your code actually uses.
The pricing tier of an App Service plan:
- Shared compute: Free and Shared, the two base tiers, runs an app on the same Azure VM as other App Service apps, including apps of other customers. These tiers allocate CPU quotas to each app that runs on the shared resources, and the resources cannot scale out.
- Dedicated compute: The Basic, Standard, Premium, and PremiumV2 tiers run apps on dedicated Azure VMs. Only apps in the same App Service plan share the same compute resources. The higher the tier, the more VM instances are available to you for scale-out.
- Isolated: This tier runs dedicated Azure VMs on dedicated Azure Virtual Networks. It provides network isolation on top of compute isolation to your apps. It provides the maximum scale-out capabilities.
Azure Container Instances (ACI)
- Docs: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/container-instances/
- Azure Container Instances offers the fastest and simplest way to run a container in Azure without having to manage any virtual machines or adopt any additional services.
- It is a PaaS offering that allows you to upload your containers, which it will run for you.
- Fast startup times: Containers offer significant startup benefits over virtual machines (VMs).
- Similar to Elastic Container Service ECS, and Fargate (in AWS)
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Docs: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a complete orchestration service for containers with distributed architectures and large volumes of containers.
- Orchestration is the task of automating and managing a large number of containers and how they interact.
- Similar to Elastic Kubernetes Service EKS (in AWS)
2.2.B. describe products available for Networking such as Virtual Network, Load Balancer, VPN Gateway, Application Gateway and Content Delivery Network
Azure network services (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/?product=networking)
Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
- VNet is the fundamental building block for your private network in Azure.
- Azure Virtual Network enables many types of Azure resources such as Azure VMs to securely communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises networks.
- A virtual network is scoped to a single region; however, multiple virtual networks from different regions can be connected using virtual network peering.
- With Azure Virtual Network you can provide isolation, segmentation, communication with on-premises and cloud resources, routing and filtering of network traffic.
- VPC Virtual Private Cloud (in AWS)
Concepts
- Address space: When creating a VNet, you must specify a custom private IP address space using public and private (RFC 1918) addresses.
- Subnets: Subnets enable you to segment the virtual network into one or more sub-networks and allocate a portion of the virtual network’s address space to each subnet.
- Regions: VNet is scoped to a single region/location;
- Subscription: VNet is scoped to a subscription.
VPN Gateway
- Connects Azure virtual networks to other Azure virtual networks, or customer on-premises networks (Site To Site). Allows end users to connect to Azure services through VPN tunneling (Point To Site).
- Point-to-site VPN (VPN over SSTP Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol): Established between a virtual network and a single computer in your network.
- Site-to-site VPN (IPsec/IKE VPN tunnel): Established between your on-premises VPN device and an Azure VPN Gateway that is deployed in a virtual network.
- Each virtual network can have only one VPN gateway.
- However, you can create multiple connections to the same VPN gateway.
- When you create multiple connections to the same VPN gateway, all VPN tunnels share the available gateway bandwidth.
Azure Application Gateway (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/application-gateway/overview)
- Application Gateway is a layer 7 (Application layer) load balancer. It supports SSL termination, cookie-based session affinity, and round robin for load-balancing traffic.
- Application Load Balancer in AWS
- Application Gateway can make routing decisions based on additional attributes of an HTTP request, for example URI path or host headers.
Azure Load Balancer (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/load-balancer/load-balancer-overview)
- Azure Load Balancer can provide scale for your applications and create high availability for your services.
- Azure Load Balancer load-balances traffic at layer 4 (transport layer TCP or UDP).
- Load Balancer supports inbound and outbound scenarios, provides low latency and high throughput, and scales up to millions of flows for all Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) applications.
- Network Load Balancer (in AWS)
- A public load balancer can provide outbound connections for virtual machines (VMs) inside your virtual network. These connections are accomplished by translating their private IP addresses to public IP addresses. Public Load Balancers are used to load balance internet traffic to your VMs.
- An internal (or private) load balancer is used where private IPs are needed at the frontend only. Internal load balancers are used to load balance traffic inside a virtual network. A load balancer frontend can be accessed from an on-premises network in a hybrid scenario.
- Comparison of Standard Load Balancer vs Basic Load Balancer: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/load-balancer/skus
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- A global content delivery network that delivers audio, video, applications, images, and other files.
- CDN is a distributed network of servers that can efficiently deliver web content to users.
- CDNs store cached content on edge servers in point-of-presence (POP) locations that are close to end users, to minimize latency.
- CloudFront (AWS)
- Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) includes four products:
- Azure CDN Standard from Microsoft,
- Azure CDN Standard from Akamai,
- Azure CDN Standard from Verizon, and
- Azure CDN Premium from Verizon.
2.2.C. describe products available for Storage such as Blob Storage, Disk Storage, File Storage, and Archive Storage
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/define-core-azure-services-products/9-define-azure-data-categories
Azure Storage https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/
- Azure Blobs: A massively scalable object store for text and binary data. Also includes support for big data analytics through Data Lake Storage Gen2.
- Azure Files: Managed file shares for cloud or on-premises deployments.
- Azure Queues: A messaging store for reliable messaging between application components.
- Azure Tables: A NoSQL store for schemaless storage of structured data.
- Azure Disks: Block-level storage volumes for Azure VMs.
Each service is accessed through a storage account. To get started, see Create a storage account.
Blob Storage docs-Overview | docs-Comparison
-
Azure Blob storage is Microsoft’s object storage solution for the cloud. Blob storage is optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured data, such as text or binary data.
-
Blob storage offers three types of resources:
-
The storage account A storage account provides a unique namespace in Azure for your data. Every object that you store in Azure Storage has an address that includes your unique account name. The combination of the account name and the Azure Storage blob endpoint forms the base address for the objects in your storage account.
-
A container in the storage account A container organizes a set of blobs, similar to a directory in a file system. A storage account can include an unlimited number of containers, and a container can store an unlimited number of blobs.
-
A blob in a container Azure Storage supports three types of blobs:
- Block blobs store text and binary data. Block blobs are made up of blocks of data that can be managed individually. Block blobs store up to about 4.75 TiB of data. Larger block blobs are available in preview, up to about 190.7 TiB
- Append blobs are made up of blocks like block blobs, but are optimized for append operations. Append blobs are ideal for scenarios such as logging data from virtual machines.
- Page blobs store random access files up to 8 TB in size. Page blobs store virtual hard drive (VHD) files and serve as disks for Azure virtual machines. For more information about page blobs, see Overview of Azure page blobs.
-
-
Azure storage offers different access tiers, which allow you to store blob object data in the most cost-effective manner. The available access tiers include:
- Hot - Optimized for storing data that is accessed frequently.
- Cool - Optimized for storing data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 30 days.
- Archive - Optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days with flexible latency requirements (on the order of hours). (Archive Storage)
-
Azure block blob storage offers two different performance tiers:
- Premium: optimized for high transaction rates and single-digit consistent storage latency. Example workloads: interactive workloads (interactive updates and user feedback); analytics; artificial intelligence; data transformation.
- Standard: optimized for high capacity and high throughput. Example workloads: backup and disaster recovery datasets; media content; bulk data processing.
Storage Account overview https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/storage/common/storage-account-overview#types-of-storage-accounts
Azure Storage offers several types of storage accounts.
- General-purpose v2 accounts: Basic storage account type for blobs, files, queues, and tables. Recommended for most scenarios using Azure Storage.
- General-purpose v1 accounts: Legacy account type for blobs, files, queues, and tables. Use general-purpose v2 accounts instead when possible.
- BlockBlobStorage accounts: Storage accounts with premium performance characteristics for block blobs and append blobs. Recommended for scenarios with high transactions rates, or scenarios that use smaller objects or require consistently low storage latency.
- FileStorage accounts: Files-only storage accounts with premium performance characteristics. Recommended for enterprise or high performance scale applications.
- BlobStorage accounts: Legacy Blob-only storage accounts. Use general-purpose v2 accounts instead when possible.
Azure Storage redundancy
- Azure Storage always stores multiple copies of your data so that it is protected from planned and unplanned events, including transient hardware failures, network or power outages, and massive natural disasters.
Primary Region redundancy
- Data in an Azure Storage account is always replicated three times in the primary region.
-
Azure Storage offers two options for how your data is replicated in the primary region:
- Locally redundant storage (LRS)
- copies your data synchronously three times within a single physical location in the primary region.
- LRS is the least expensive replication option, but is not recommended for applications requiring high availability.
- LRS provides at least 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability of objects over a given year.
- Zone-redundant storage (ZRS)
- copies your data synchronously across three Azure availability zones in the primary region.
- For applications requiring high availability, Microsoft recommends using ZRS in the primary region, and also replicating to a secondary region.
- ZRS offers durability for Azure Storage data objects of at least 99.9999999999% (12 9’s) over a given year.
- Locally redundant storage (LRS)
Secondary Region redundancy
- For applications requiring high availability, you can choose to additionally copy the data in your storage account to a secondary region that is hundreds of miles away from the primary region.
-
Azure Storage offers two options for copying your data to a secondary region:
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
- Data is replicated synchronously three times in the primary region using locally redundant storage (LRS), then replicated asynchronously to the secondary region.
- GRS offers durability for Azure Storage data objects of at least 99.99999999999999% (16 9’s) over a given year.
- Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS)
- Data is replicated synchronously across three Azure availability zones in the primary region using zone-redundant storage (ZRS), then replicated asynchronously to the secondary region.
- GZRS is designed to provide at least 99.99999999999999% (16 9’s) durability of objects over a given year.
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
- With GRS or GZRS, the data in the secondary location isn’t available for read or write access unless there is a failover to the secondary region.
- For read access to the secondary location, configure your storage account to use read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS) or read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS).
-
Within the secondary location, data is always replicated synchronously three times using LRS. LRS in the secondary region protects your data against hardware failures.
Disk Storage / Azure Managed Disks
- Disk storage provides disks for virtual machines, applications, and other services to access and use as they need, similar to how they would in on-premises scenarios. LRS protects your data against server rack and drive failures.
- Disk storage allows data to be persistently stored and accessed from an attached virtual hard disk.
- AWS Elastic Block Store (EBS)
- Benefits of managed disks:
- Highly durable and available, 99.999% availability.
- Simple and scalable VM deployment.
- Integration with availability sets.
- Integration with Availability Zones.
- Azure Backup support to create a backup job with time-based backups and backup retention policies.
- Granular access control using RBAC (Azure Role-based access control).
- Upload your vhd - Direct upload makes it easy to transfer your vhd to an Azure managed disk.
- Disk types:
| Detail | Ultra disk | Premium SSD | Standard SSD | Standard HDD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disk type | SSD | SSD | SSD | HDD |
| Scenario | IO-intensive workloads such as [SAP HANA], top tier databases (for example, SQL, Oracle), and other transaction-heavy workloads. | Production and performance sensitive workloads | Web servers, lightly used enterprise applications and dev/test | Backup, non-critical, infrequent access |
| Max disk size | 65,536 gibibyte (GiB) | 32,767 GiB | 32,767 GiB | 32,767 GiB |
| Max throughput | 2,000 MB/s | 900 MB/s | 750 MB/s | 500 MB/s |
| Max IOPS | 160,000 | 20,000 | 6,000 | 2,000 |
Azure Files / File Storage (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/files/storage-files-introduction)
- Azure Files enables you to set up highly available network file shares that can be accessed by using the standard Server Message Block (SMB) protocol.
- Azure file shares can be mounted concurrently by cloud or on-premises deployments of Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- Additionally, Azure file shares can be cached on Windows Servers with Azure File Sync for fast access near where the data is being used.
- You can also read the files using the REST interface or the storage client libraries.
- AWS FSx for Windows File Server
Azure file shares can be used to:
- Replace or supplement on-premises file servers or NAS devices.
- “Lift and shift” applications: Azure Files makes it easy to “lift and shift” applications to the cloud that expect a file share to store file application or user data.
- Simplify cloud development, e.g.: shared application settings, via REST API or SMB share; diagnostic share logs, metrics and crash dumps;
Azure Queue service (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/queues/storage-queues-introduction)
- Queue service is used to store and retrieve messages.
- Queue messages can be up to 64 KB in size, and a queue can contain millions of messages.
- Queues are generally used to store lists of messages to be processed asynchronously.
- AWS Simple Queue Service (SQS)
Azure Table storage (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/tables/table-storage-overview)
- Azure Table storage is a service that stores structured NoSQL data in the cloud, providing a key/attribute store with a schemaless design.
- Table storage is a NoSQL datastore which accepts authenticated calls from inside and outside the Azure cloud.
- You can use Table storage to store and query huge sets of structured, non-relational data, and your tables will scale as demand increases.
- Amazon DynamoDB (in AWS)
- There is now a premium offering for table storage: the Azure Cosmos DB Table API. This API offers throughput-optimized tables, global distribution, and automatic secondary indexes. There are some feature differences between Table API in Azure Cosmos DB and Azure table storage and Benefits of moving to Cosmos DB Table API.
IF YOU WANT TO… USE THIS
- Get scalable and secure storage for your virtual machines: Disk storage
- Find massively scalable, secure storage for your unstructured data: Blob storage
- Get low-cost storage for rarely accessed data: Archive Storage
- Get secure cloud file shares: File Storage
- Get secure storage for message-based communication between apps: Queue Storage
- Appliances and solutions for data transfer to Azure and edge compute: Data Box
- Create powerful file shares for enterprise workloads, including open-source/Linux: Azure NetApp Files
- File caching for high-performance computing (HPC): Azure HPC Cache
2.2.D. describe products available for Databases such as Cosmos DB, Azure SQL Database, Azure Database for MySQL, Azure Database for PostgreSQL, Azure Database Migration service
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/?product=databases
More on Azure databases: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/product-categories/databases/
Cosmos DB (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/cosmos-db/)
- Azure Cosmos DB is a fully managed NoSQL database service for modern app development with guaranteed single-digit millisecond response times and 99.999-per cent availability, backed by SLAs, automatic and instant scalability, and open-source APIs for MongoDB and Cassandra.
- It supports schema-less data that lets you build highly responsive and Always On applications to support constantly changing data.
- Azure Cosmos DB free tier makes it easy to get started, develop and test your applications, or even run small production workloads for free. When free tier is enabled on an account, you’ll get the first 400 RU/s and 5 GB of storage in the account free. More info: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/cosmos-db/optimize-dev-test#azure-cosmos-db-free-tier
- Key benefits:
- Turnkey global distribution. CosmosDB transparently replicates data to any Azure regions at any time, with a click of a button.
- Always On. High availability of 99.999% for both reads and writes.
- Elastic scalability of throughput and storage, worldwide. Designed with transparent horizontal partitioning and multi-master replication, Cosmos DB offers unprecedented elastic scalability for your writes and reads, all around the globe.
- Guaranteed low latency at 99th percentile, worldwide.
- Precisely defined, multiple consistency choices.
- No schema or index management.
- Battle tested database service, a foundational service in Azure, and used by many of Microsoft’s products for mission critical applications at global scale.
- Ubiquitous regional presence, available in all Azure regions worldwide.
- Secure by default and enterprise ready; encrypted at rest and in transit, row level authorization, and adheres to strict security standards.
- Significant TCO savings; fully managed service.
- Industry leading comprehensive SLAs; 99.999% high availability, read and write latency at the 99th percentile, guaranteed throughput, and consistency.
- Globally distributed operational analytics and AI with natively built-in Apache Spark.
- Develop applications on Cosmos DB using popular Open Source Software (OSS) APIs, i.e. Cassandra, MongoDB, Gremlin, and Azure Table Storage.
Azure SQL (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/azure-sql/)
Azure SQL family of SQL Server database engine products in the cloud:
- Azure SQL Database,
- Azure SQL Managed Instance, and
- SQL Server on Azure VM.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/azure-sql/azure-sql-iaas-vs-paas-what-is-overview
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/azure-sql/database/features-comparison
Azure SQL Database (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/azure-sql/database/sql-database-paas-overview)
- Azure SQL Database is a relational database as a service (DaaS) based on the latest stable version of Microsoft SQL Server database engine.
- Best for modern cloud applications that want to use the latest stable SQL Server features and have time constraints in development and marketing.
- A fully managed SQL Server database engine, based on the latest stable Enterprise Edition of SQL Server.
- Deployment options:
- Single database (Hyperscale storage (up to 100TB), serverless compute, easy management);
- Elastic pool (resource sharing for cost optimization, simplified performance management);
- Database server (access management, backup management, business continuity management)
Azure SQL Managed Instance
- The broadest SQL Server compatibility on a fully managed service streamlines app modernisation with minimal code changes.
- Lift and shift ready.
- Best for new applications or existing on-premises applications that want to use the latest stable SQL Server features and that are migrated to the cloud with minimal changes.
- Native virtual network support
- Fully managed service, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Azure SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines
- Best for migrations and applications requiring OS-level access.
- Rapid development and test scenarios when you do not want to buy on-premises non-production SQL Server hardware.
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- Lift and shift ready
- Expansive SQL Server and OS version support
- Automated manageability features for SQL Server
Azure Database for MySQL (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/mysql/)
- Fully managed database that supports the latest MySQL community editions.
- Azure Database for MySQL is easy to set up, manage and scale.
- It automates the management and maintenance of your infrastructure and database server, including routine updates, backups and security.
- Deliver high availability and elastic scaling to open-source mobile and web apps with a managed community MySQL database service, or migrate MySQL workloads to the cloud.
Azure Database for PostgreSQL (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/postgresql/)
- Build scalable, secure and fully managed enterprise-ready apps on open-source PostgreSQL.
- Scale out single-node PostgreSQL with high performance or migrate PostgreSQL and Oracle workloads to the cloud.
- Two deployment options: Single Server and Hyperscale (Citus).
- Single Server deployment option delivers:
- Built-in high availability with no additional cost (99.99% SLA)
- Predictable performance, using inclusive pay-as-you-go pricing
- Vertical scale as needed within seconds
- Monitoring and alerting to assess your server
- Enterprise-grade security and compliance
- Secured to protect sensitive data at-rest and in-motion
- Automatic backups and point-in-time-restore for up to 35 days
- Three pricing tiers: Basic, General Purpose, and Memory Optimized.
- Hyperscale (Citus) cluster
- Hyperscale (Citus) is a new deployment option for Azure Database for PostgreSQL that scales out Postgres horizontally. A Hyperscale (Citus) database cluster is a group of nodes that are running Postgres, including 1 coordinator node and 2 or more worker nodes.
- Hyperscale (Citus) has a minimum database cluster size of 3 nodes: 1 coordinator node and 2 worker nodes. Maximum cluster can scale out to 100s of nodes.
- The Hyperscale (Citus) deployment option delivers:
- Horizontal scaling across multiple machines using sharding
- Query parallelization across these servers for faster responses on large datasets
- Excellent support for multi-tenant applications, real time operational analytics, and high throughput transactional workloads
Azure Database for MariaDB (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/mariadb/)
- Deliver high availability and elastic scaling to open-source mobile and web apps with a managed community MariaDB database service.
- is based on the MariaDB community edition (available under the GPLv2 license) database engine, version 10.2 and 10.3.
Azure Database Migration service
- The Azure Database Migration Service is a fully managed service designed to enable seamless migrations from multiple database sources to Azure data platforms with minimal downtime (online migrations).
- The service uses the Microsoft Data Migration Assistant to generate assessment reports that provide recommendations to help guide you through required changes prior to performing a migration.
- Supported sources and migration scenarios, e.g. SQL Server, RDS SQL, MongoDB, MySQL, RDS MySQL, PostgreSQL, RDS PostgreSQL, Oracle.
Azure Cache for Redis (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/azure-cache-for-redis/)
- An in-memory–based, distributed caching service that provides a high-performance store typically used to offload nontransactional work from a database.
- With Azure Cache for Redis, performance is improved by copying frequently accessed data to in-memory storage instead of being loaded from disk by a database.
- a secure, dedicated Redis cache, managed by Microsoft, hosted on Azure, and accessible to any application within or outside of Azure.
2.2.E. describe the Azure Marketplace and its usage scenarios
Azure Marketplace is a service on Azure that helps connect end users with Microsoft partners, independent software vendors (ISVs), and start-ups that are offering their solutions and services, which are optimized to run on Azure.
Azure Marketplace allows customers—mostly IT professionals and cloud developers—to find, try, purchase, and provision applications and services from hundreds of leading service providers, all certified to run on Azure.
Using Azure Marketplace, you can provision end-to-end solutions quickly and reliably, hosted in your own Azure environment. At the time of writing, this includes over 8,000 listings.
2.3. Describe some of the solutions available on Azure
2.3.A. describe Internet of Things (IoT) and products that are available for IoT on Azure such as IoT Hub and IoT Central
Internet of Things (IoT)
Internet of Things (IoT) is the ability for devices to garner and then relay information for data analysis.
Azure Internet of Things (IoT) is a collection of Microsoft-managed cloud services that connect, monitor, and control billions of IoT assets. In simpler terms, an IoT solution is made up of one or more IoT devices that communicate with one or more back-end services hosted in the cloud.
An IoT device is typically made up of a circuit board with sensors attached that use WiFi to connect to the internet. For example:
- A pressure sensor on a remote oil pump.
- Temperature and humidity sensors in an air-conditioning unit.
- An accelerometer in an elevator.
- Presence sensors in a room.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-fundamentals/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-fundamentals/iot-services-and-technologies
IoT Hub https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/iot-hub/
Azure IoT Hub is a managed service hosted in the cloud that acts as a central message hub for bi-directional communication between your IoT application and the devices it manages.
- build IoT solutions with reliable and secure communications between millions of IoT devices and a cloud-hosted solution backend.
- supports communications both from the device to the cloud and from the cloud to the device.
- supports multiple messaging patterns such as device-to-cloud telemetry, file upload from devices, and request-reply methods to control your devices from the cloud.
- IoT Hub monitoring helps you maintain the health of your solution by tracking events such as device creation, device failures, and device connections.
- Use Azure IoT platform services such as Azure IoT Hub and the Azure IoT device SDKs to build a custom IoT solution from scratch.
IoT Central https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/iot-central/
IoT Central is a fully managed global IoT software as a service (SaaS) solution that makes it easy to connect, monitor, and manage your IoT assets at scale.
- a fully managed application platform that you can use to create custom IoT solutions.
- provides seamless device connectivity and management.
- IoT Central uses application templates to create solutions.
IoT Edge https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/iot-edge/
Azure IoT Edge extends IoT Hub. Analyze device data locally instead of in the cloud to send less data to the cloud, react to events quickly, and operate offline.
- Azure IoT Edge moves cloud analytics and custom business logic to devices so that your organization can focus on business insights instead of data management.
- Scale out your IoT solution by packaging your business logic into standard containers, then you can deploy those containers to any of your devices and monitor it all from the cloud.
- Azure IoT Edge is made up of three components:
- IoT Edge modules are containers that run Azure services, third-party services, or your own code. Modules are deployed to IoT Edge devices and execute locally on those devices.
- The IoT Edge runtime runs on each IoT Edge device and manages the modules deployed to each device.
- A cloud-based interface enables you to remotely monitor and manage IoT Edge devices.
2.3.B. describe Big Data and Analytics and products that are available for Big Data and Analytics such as Azure Synapse Analytics, HDInsight, and Azure Databricks
Big data and analytics
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/learn/modules/identify-azure-solutions/4-explore-big-data-analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/synapse-analytics/sql-data-warehouse/) | https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/synapse-analytics/overview-what-is
Azure Synapse Analytics (formerly Azure SQL Data Warehouse) is a limitless analytics service that brings together enterprise data warehousing and big data analytics.
- Cloud-based Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW) that uses Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) to quickly run complex queries across petabytes of data.
- Similar to AWS Redshift
- Azure Synapse has four components:
- Synapse SQL: Complete T-SQL based analytics – Generally Available
- SQL pool (pay per DWU provisioned)
- SQL on-demand (pay per TB processed) (preview)
- Spark: Deeply integrated Apache Spark (preview)
- Synapse Pipelines: Hybrid data integration (preview)
- Studio: Unified user experience. (preview)
- Synapse SQL: Complete T-SQL based analytics – Generally Available
HDInsight (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/hdinsight/hdinsight-overview)
- Azure HDInsight is a managed Apache Hadoop service that lets you run Apache Spark, Apache Hive, Apache Kafka, Apache HBase, and more in the cloud.
- Azure HDInsight is a fully managed, open-source analytics service in the cloud for enterprises.
- It is a cloud service that makes it easier, faster, and more cost-effective to process massive amounts of data.
- HDInsight run popular open-source frameworks and create cluster types such as Apache Spark, Apache Hadoop, Apache Kafka, Apache HBase, Apache Storm, Machine Learning Services, Apache Interactive Query.
- supports a broad range of scenarios such as extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL); data warehousing; machine learning; and IoT.
- Similar to AWS EMR (Elastic MapReduce)
What is Apache Hadoop in Azure HDInsight?
Apache Hadoop was the original open-source framework for distributed processing and analysis of big data sets on clusters. The Hadoop ecosystem includes related software and utilities, including Apache Hive, Apache HBase, Spark, Kafka, and many others.
Azure Databricks (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/databricks/)
- Big data analytics and AI with optimised Apache Spark.
- A fully managed, fast, easy and collaborative Apache Spark based analytics platform optimised for Azure.
- Similar to AWS EMR (Elastic MapReduce)
Azure Data Lake Analytics (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/data-lake-analytics/ | https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/services/data-lake-analytics/)
- Azure Data Lake Analytics is an on-demand analytics job service that simplifies big data.
- Instead of deploying, configuring, and tuning hardware, you write queries to transform your data and extract valuable insights.
- The analytics service can handle jobs of any scale instantly by setting the dial for how much power you need.
- You only pay for your job when it is running, making it cost-effective.
- Similar to AWS Kinesis Analytics
More info on big data and analytics.
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/product-categories/analytics/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/?product=analytics
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/data-lake-analytics/data-lake-analytics-overview
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/data-guide/big-data/
2.3.C. describe Artificial Intelligence (AI) and products that are available for AI such as Azure Machine Learning Service and Studio
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Machine Learning is a data science technique that allows computers to use existing data to forecast future behaviors, outcomes, and trends.
- Using machine learning, computers learn without being explicitly programmed.
- Forecasts or predictions from machine learning can make apps and devices smarter.
Azure Machine Learning Service (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/machine-learning/)
- The Azure Machine Learning service provides a cloud-based environment you can use to develop, train, test, deploy, manage, and track machine learning models.
- The Azure Machine Learning service can auto-generate a model and auto-tune it for you. It will let you start training on your local machine, and then scale out to the cloud. When you have the right model, you can easily deploy it in a container such as Docker in Azure.
Compare Azure Machine Learning vs Machine Learning Studio (classic)
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/machine-learning/compare-azure-ml-to-studio-classic
- Azure Machine Learning provides Python and R SDKs and the “drag-and-drop” designer to build and deploy machine learning models.
- Studio (classic) only offers a standalone drag-and-drop experience.
| Feature | Machine Learning Studio (classic) | Azure Machine Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Drag and drop interface | Supported | Supported - Azure Machine Learning designer (preview) (Requires Enterprise workspace) |
| Experiment | Scalable (10-GB training data limit) | Scale with compute target |
| Training compute targets | Proprietary compute target, CPU support only | Wide range of customizable training compute targets. Includes GPU and CPU support |
| Deployment compute targets | Proprietary web service format, not customizable | Wide range of customizable deployment compute targets. Includes GPU and CPU support |
| ML Pipeline | Not supported | Build flexible, modular pipelines to automate workflows |
| MLOps | Basic model management and deployment | Entity versioning (model, data, workflows), workflow automation, integration with CICD tooling, and more |
| Model format | Proprietary format, Studio (classic) only | Multiple supported formats depending on training job type |
| Automated model training and hyperparameter tuning | Not supported | Supported in the SDK and visual workspace |
| Data drift detection | Not supported | Supported in SDK and visual workspace |
The machine learning model workflow generally follows this sequence:
- Train
- Develop machine learning training scripts in Python, R, or with the visual designer.
- Create and configure a compute target.
- Submit the scripts to a configured compute target to run in that environment. During training, the scripts can read from or write to datastores. The logs and output produced during training are saved as runs in the workspace and grouped under experiments.
- Package - After a satisfactory run is found, register the persisted model in the model registry.
- Validate - Query the experiment for logged metrics from the current and past runs. If the metrics don’t indicate a desired outcome, loop back to step 1 and iterate on your scripts.
- Deploy - Develop a scoring script that uses the model and Deploy the model as a web service in Azure, or to an IoT Edge device.
- Monitor - Monitor for data drift between the training dataset and inference data of a deployed model. When necessary, loop back to step 1 to retrain the model with new training data.
Azure Cognitive Services (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/cognitive-services/)
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/learn/modules/identify-azure-solutions/5-explore-artificial-intelligence
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/services/#ai-machine-learning
Cognitive services are a collection of domain-specific pre-trained AI models that can be customized with your data. They are categorized broadly into vision, speech, language, and search.
- Azure Cognitive Services are APIs, SDKs, and services available to help developers build intelligent applications without having direct AI or data science skills or knowledge.
- Azure Cognitive Services enable developers to easily add cognitive features into their applications.
- The goal of Azure Cognitive Services is to help developers create applications that can see, hear, speak, understand, and even begin to reason. - The catalog of services within Azure Cognitive Services can be categorized into five main pillars - Vision, Speech, Language, Web Search, and Decision.
Five categories are:
- Knowledge: Knowledge services create rich knowledge resources that integrate into apps and services.
- Language: Language services can understand the meaning of unstructured text or recognize the speaker’s intent.
- Search: Enable apps and services to harness the power of a web-scale, ad-free search engine. Use search services to find information across billions of web pages, images, videos, and news search results.
- Speech: Speech services can convert spoken language into text, or produce natural-sounding speech from text using standard (or customizable) voice fonts.
- Vision: Vision makes it possible for apps and services to accurately identify and analyze content within images and videos.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/cognitive-services/cognitive-services-and-machine-learning
- Decision: Build apps that surface recommendations for informed and efficient decision-making.
- Language: Allow your apps to process natural language with pre-built scripts, evaluate sentiment and learn how to recognize what users want.
- Search: Add Bing Search APIs to your apps and harness the ability to comb billions of webpages, images, videos, and news with a single API call.
- Speech: Convert speech into text and text into natural-sounding speech. Translate from one language to another and enable speaker verification and recognition.
- Vision: Recognize, identify, caption, index, and moderate your pictures, videos, and digital ink content.
2.3.D. describe Serverless computing and Azure products that are available for serverless computing such as Azure Functions, Logic Apps, and Event Grid
Serverless computing is a cloud-hosted execution environment that runs your code but abstracts the underlying hosting environment. You create an instance of the service and you add your code. No infrastructure configuration or maintenance is required, or even allowed.
Azure Functions (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/)
- Azure Functions is a serverless compute service that lets you run event-triggered code without having to explicitly provision or manage infrastructure.
- Functions are ideal when you’re only concerned with the code running your service and not the underlying platform or infrastructure.
- Functions are commonly used when you need to perform work in response to an event—often via a REST request, timer, or message from another Azure service—and when that work can be completed quickly, within seconds or less.
- Scale automatically,
- Charges accrue only when a function is triggered,
- Stateless
- Similar to AWS Lambda
Azure Logic Apps (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/logic-apps/)
- Logic Apps is a cloud service that helps you automate and orchestrate tasks, business processes, and workflows when you need to integrate apps, data, systems, and services across enterprises or organizations.
- Logic Apps are designed in a web-based designer and can execute logic triggered by Azure services without writing any code.
- Every logic app workflow starts with a trigger, which fires when a specific event happens, or when new available data meets specific criteria.
- AWS Step Functions; Simple Workflow Service (SWF)
Azure Event Grid (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/event-grid/overview)
Event Grid allows you to easily build applications with event-based architectures.
- A fully managed event routing service that allows for uniform event consumption using a publish/subscribe model.
- AWS SNS Simple Notification Service
2.3.E. describe DevOps solutions available on Azure such as Azure DevOps and Azure DevTest Labs
DevOps (Development and Operations) brings together people, processes, and technology, automating software delivery to provide continuous value to your users. Azure DevOps Services allows you to create, build, and release pipelines that provide continuous integration, delivery, and deployment for your applications.
DevOps Services
- DevOps Services provides development collaboration tools including high-performance pipelines, free private Git repositories, configurable Kanban boards, and extensive automated and cloud-based load testing.
- DevOps Services was formerly known as Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS).
Azure Lab Services (https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/services/devtest-lab/)
- Lab Services is a service that helps developers and testers quickly create environments in Azure, while minimizing waste and controlling cost.
- Users can test their latest application versions by quickly provisioning Windows and Linux environments using reusable templates and artifacts. You can easily integrate your deployment pipeline with DevTest Labs to provision on-demand environments.
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/devtest-labs/devtest-lab-overview
Azure DevTest Labs - This service enables you to quickly set up an environment for your team (for example: development environment, or test environment in the cloud). A lab owner creates a lab, provisions Windows, or Linux virtual machines, installs the necessary software and tools, and makes them available to lab users. Lab users connect to virtual machines (VMs) in the lab, and use them for their day-to-day work, short-term projects. Once users start utilizing resources in the lab, a lab admin can analyze cost and usage across multiple labs, and set overarching policies to optimize your organization or team’s costs.
Azure Lab Services - This service lets you create managed lab types. Currently, classroom labs is the only type of managed lab that’s supported by Azure Lab Services. The service itself handles all the infrastructure management for a managed lab type, from spinning up VMs to handling errors, and scaling the infrastructure. After an IT admin creates a lab account in Azure Lab Services, an instructor can quickly set up a lab for his class, specify the number and type of VMs that are need to exercises in the class, and add users to the class. Once a user registers to the class, the user can access the VM to do exercises for the class.
You can create two types of labs: managed lab types with Azure Lab Services and labs with Azure Lab Services (DevTest Labs).
| Features | Managed lab types | DevTest Labs |
|---|---|---|
| Management of Azure infrastructure in the lab. | Automatically managed by the service | You manage on your own |
| Built-in resiliency to infrastructure issues | Automatically handled by the service | You manage on your own |
| Subscription management | Service handles allocation of resources within Microsoft subscriptions backing the service. Scaling is automatically handled by the service. | You manage on your own in your own Azure subscription. No autoscaling of subscriptions. |
| Azure Resource Manager deployment within the lab | Not available | Available |
2.3.F. describe the benefits and outcomes of using Azure solutions
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/intro-to-data-in-azure/2-benefits-of-using-azure-to-store-data https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/intro-to-data-in-azure/4-comparison-azure-and-on-prem-storage
2.4. Describe Azure management tools
Azure Management tools.
There are tools available for the command line, language-specific Software Development Kits (SDKs), developer tools, tools for migration, and many others.
2.4.A. describe Azure tools such as Azure Portal, Azure PowerShell, Azure CLI and Cloud Shell
Azure portal
The Azure portal is a public website that you can access with any web browser. After you sign in with your Azure account, you can create, manage, and monitor any available Azure services. You can identify a service you’re looking for, get links for help on a topic, and deploy, manage, and delete resources. It also guides you through complex administrative tasks using wizards and tooltips.
The dashboard view provides high-level details about your Azure environment. You can customize the portal view as you need by moving and resizing tiles, displaying particular services of interest, accessing links for help and support, and providing feedback.
Azure PowerShell (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/azure/?view=azps-4.4.0)
Azure PowerShell is a module that you add to Windows PowerShell or PowerShell Core that enables you to connect to your Azure subscription and manage resources. Azure PowerShell requires Windows PowerShell to function. PowerShell provides services such as the shell window and command parsing. Azure PowerShell then adds the Azure-specific commands.
Azure CLI (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/?view=azure-cli-latest)
Azure CLI is a cross-platform command-line program that connects to Azure and executes administrative commands on Azure resources. Cross platform means that it can be run on Windows, Linux, or macOS.
Cloud Shell
Azure Cloud Shell is a browser-based scripting environment in your portal. It provides the flexibility of choosing the shell experience that best suits the way you work. Linux users can opt for a Bash experience, while Windows users can opt for PowerShell.
A storage account is required to use the Cloud Shell and you will be prompted to create one when accessing the Azure Cloud Shell.
Azure Mobile App
Microsoft Azure mobile app allows you to access, manage, and monitor all your Azure accounts and resources from your iOS or Android phone or tablet.
Azure REST API
Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs are service endpoints that support sets of HTTP operations (methods), which provide create, retrieve, update, or delete access to the service’s resources. A REST API defines a set of functions which developers can perform requests and receive responses via HTTP protocol such as GET and POST.
2.4.B. describe Azure Advisor (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/advisor/advisor-overview)
Advisor is a personalized cloud consultant that helps you follow best practices to optimize your Azure deployments. It analyzes your resource configuration and usage telemetry and then recommends solutions that can help you improve the cost effectiveness, performance, Reliability (formerly called High availability), and security of your Azure resources.
- Get proactive, actionable, and personalized best practices recommendations.
- Improve the performance, security, and high availability of your resources as you identify opportunities to reduce your overall Azure costs.
- Get recommendations with proposed actions inline.
Recommendations are divided into five categories:
- Reliability (formerly called High Availability): To ensure and improve the continuity of your business-critical applications.
- Security: To detect threats and vulnerabilities that might lead to security breaches.
- Performance: To improve the speed of your applications.
- Cost: To optimize and reduce your overall Azure spending.
- Operational Excellence: To help you achieve process and workflow efficiency, resource manageability and deployment best practices.